Physician Associate Studies MSc


You are viewing Course summary
Course Summary
This course aims to inform and equip the practitioner with the necessary knowledge and skills to function in a modern clinical environment as a Physician Associate.
The physician associate is a type of health professional whose development has been led by the Department of Health and has involved the Royal College of Physicians (RCP) and Royal College of General Practitioners (RGCP), as well as the profession itself through the faculty of physician associates (FPA). This course aims to holistically develop you as a clinician, leader and pioneer of the profession.
If you have any queries about the MSc Physician Associate Studies course, please email pa@chester.ac.uk
This course is delivered by Physician Associates and other health care professionals, supplemented by a variety of Clinicians and Biomedical Scientists from local Hospital Departments and general practices.
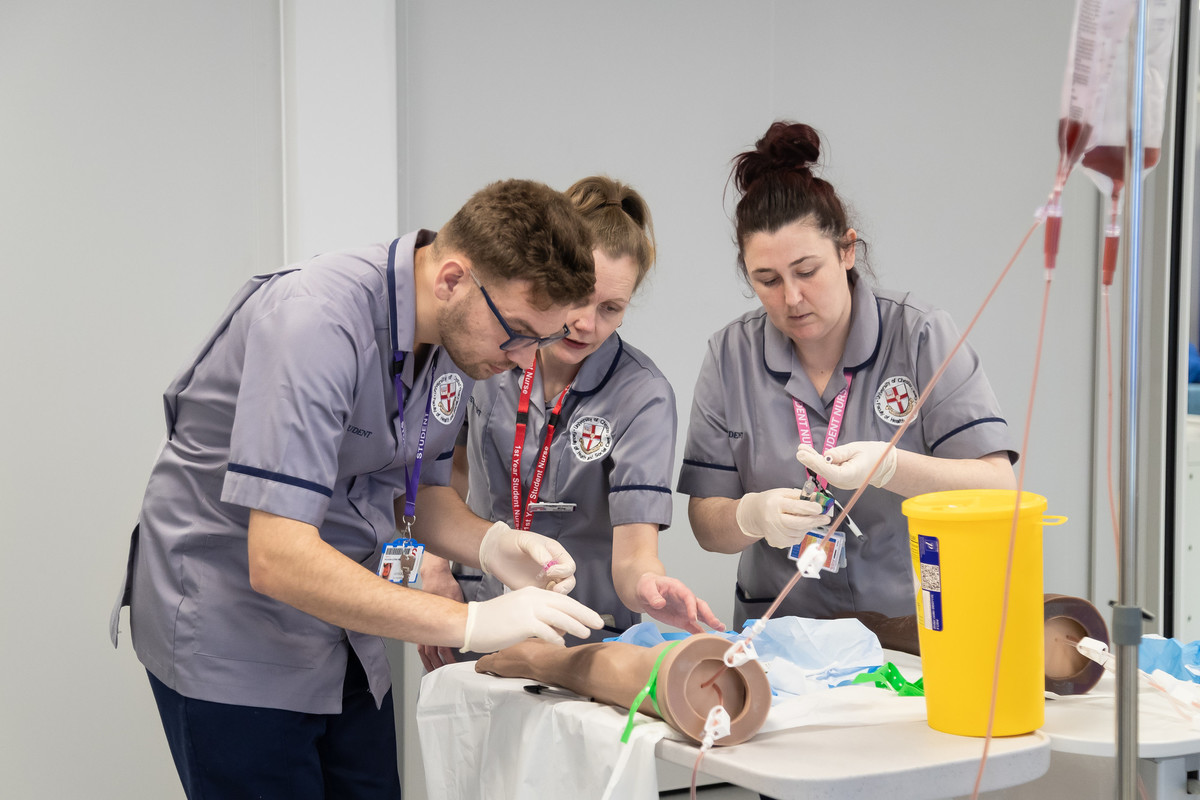
You will be trained using an integrated model of theory and practice. You will have the opportunity to hone your clinical skills and knowledge in simulation. You will have contact with our simulated patients from the first week of the course. We have an up-to-date simulation suite which allows you to learn and develop in a safe environment prior to conducting clinical placements.
What you’llStudy
Physician associates support doctors in the diagnosis and management of patients, and are trained to perform a number of roles. We have developed our course in collaboration with our regional healthcare partners. This is an intensive course with theory, clinical skills and patient contact running in parallel from the beginning.
Module content:
- Core concepts of anatomy and physiology within the core body systems (Cardiovascular, Respiratory, Neurological, Gastrointestinal, Endocrine, Ears, Eyes, Nose and Throat, Musculoskeletal)
- Investigations such as interpreting blood results, ECG’s, Chest X-Rays, Urinalysis, and Physiological parameters.
- Explore pathophysiology of core conditions (for example, Cardiovascular disease, Diabetes, COPD), the range of evidence used to inform a differential diagnosis.
- Management of patients using a holistic approach to patient education, lifestyle, social prescribing and disease prevention
Module aims:
The module aims to introduce students to the theoretical underpinning of anatomy and physiology, disease process, patient investigations, diagnosis and management.
Module content:
- Core clinical skills for year 1 taking observations, calculating and documenting National Early Warning Score (NEWS), Performing and interpreting ECGs, Peak flow assessment and inhaler technique, performing venepuncture, performing cannulation, Performing injection, perform urine dipstick, basic life support.
- Mini clinical evaluation examinations for year 1: Cardiovascular, Respiratory and Gastrointestinal (excluding PR examination) systems.
- Core communication skills with patients, relatives, carers and members of the multidisciplinary team. Recognising the importance of upholding confidentiality. Performing clinical histories in the core areas (cardiovascular, Gastrointestinal, Respiratory, Neurological, Haematological, Endocrinology systems).
- Preparation for participation in case-based discussion, aspects of person centred care, respecting dignity, diversity and difference. Formulating differential diagnoses and management plans.
- Personal and professional development including attitudes, knowledge, self-awareness and reflection required for professional practice as a Physician Associate. Guidance on professional and personal limitations, including practicing without impairment from substance abuse, cognitive deficiency or mental illness. Demonstrates professional behaviour and probity.
Module aims:
This module aims to provide students with practice learning opportunities across a range of general clinical areas.
Module content:
- Teamwork, professionalism, complex situations and safeguarding and impact on professional clinical practice. Definitions of evidence-based practice.
- Environmental and social influences of health e.g. age, ethnicity, class, gender, health promotions, health inequalities and epidemiology.
- Consent, capacity, safeguarding, professional body regulations, patient safety and quality improvement.
- Understanding own personal values through reflection and reflexive practice.
Module aims:
This module aims to introduce students to key aspects of values based medicine such as ethical and legal frameworks of practice, teamwork, professionalism, safeguarding and health inequalities.
Module content:
- Taking medication histories for prescribed, non-prescribed medications, herbal medicines, supplements and drugs of abuse
- Clinical therapeutics and the management of disease related to body systems this includes, but is not limited to, Cardiovascular, Respiratory, Neurological, Gastrointestinal and Haematological systems
- Practical applications of pharmacokinetics such as patient communication and drug counselling with patients, carers and other healthcare professionals, initiating treatments and using resources such as the BNF to make informed decisions
- Therapeutics, pharmacokinetics, medication side effects and interactions, including multiple treatments, long-term conditions, non-prescribed drugs, the role of antimicrobial stewardship and patient concordance in safe prescribing
Module aims:
This module introduces the core knowledge and understanding of the key pharmacological principles to common conditions that they will encounter in year one.
Module content:
- Simulated patient histories including: history of presenting complaints, past medical histories, review of body systems, medication history, identifying concerns, relevant psychological and social factors contributing to patients presenting complaints. Including communicating to patients and family in simulation.
- Simulated physical examination for example, Cardiovascular, Neurological and Gastrointestinal examinations, how to interpret clinical examination findings and their relationship to making a diagnosis.
- Core clinical procedures in a simulated environment for example venepuncture, subcutaneous injections, intramuscular injections and cannulation.
- Key stages of the clinical reasoning process to formulate the differential diagnosis.
- The stages of developing a management plan related to the core conditions
Module aims:
This module will introduce the student to a range of core clinical skills and provide opportunities to practice these skills in a simulated environment in preparation for placement.
Module content:
- The skills of effective and complex communication to establish patient trust, verbal and non-verbal communication together with professional behaviour. Communicate effectively with patients, their relatives, carers or other advocates, and with colleagues and members of the multidisciplinary team.
- Simulated physical examination skills paying particular attention to intimate and sensitive examination(s). Conducting a physical examination on any patient with special sensitivity to gender, age and cultural background formulating a differential diagnosis
- Core clinical procedures in a simulated environment for example urinary catheterisation, taking an ABG, speculum examination, surgical scrubbing.
- Formulate a detailed differential diagnosis from the interpretation of multiple and complex data sets.
- The stages of developing a management related to conditions within the core specialties, for example, paediatrics mental health
Module aims:
This module will develop students range of core and advanced clinical skills and provide opportunities to practice these skills in a simulated environment.
Module content:
- Developed concepts of anatomy and physiology related to second year teaching themes including Obstetrics and Gynaecology, neurological
(Mental health), foetal development
(Paediatrics), and Musculoskeletal systems. - Investigations such as interpreting Arterial Blood Gasses, Blood results, Abdominal X-Ray and Cervical Samples.
- Explore pathophysiology of second year-based conditions (for example, Endometriosis, Ectopic Pregnancy, complications in childbirth, Croup, psychosis), use a range of evidence to determine differential diagnosis.
- Clinical reasoning to determine most likely diagnosis, developing management plans for patients using holistic approaches to patient education, lifestyle, social prescribing and disease prevention.
Module aims:
The module aims to develop theoretical concepts undertaken in MD7126 and progress student’s knowledge of anatomy and physiology, approach to disease processes, patient investigations, diagnosis and management.
Module content:
- Core clinical skills for year 2: perform surgical scrubbing up, male and female catheterisation, arterial blood gas (ABG), obtain blood cultures, swabs, place nasogastric (NG) tubes (in simulation only), set up infusions, use different forms of local anaesthetic, perform wound care and closure and intermediate life support.
- Mini clinical evaluation examinations for year 2: Paediatric examination, Gynaecological examination including speculum exam, Obstetric examination, Musculoskeletal examination, Mental Health examination
- Core communication skills with patients, relatives, carers and members of the multidisciplinary team. Recognising the importance of upholding confidentiality. Performing clinical histories in the core areas such as Paediatrics, Gynaecology, Obstetrics, mental health and emergency medicine.
- Preparation for participation in case-based discussion, aspects of person-centred care, respecting dignity, diversity and difference. Formulating differential diagnoses and management plans.
- Personal and professional development including attitudes, knowledge, self-awareness and reflection required for professional practice as a Physician Associate. Guidance on professional and personal limitations, including practicing without impairment from substance abuse, cognitive deficiency or mental illness. Demonstrates professional behaviour and probity
Module aims:
This module aims to provide students with practice learning opportunities across a range of specialist clinical areas.
Module content:
The knowledge, critical skills and clinical knowledge that have been accumulated during the taught modules and the clinical placements will have provided the students with the ability to complete a research project. This will help students to better understand:
• The identification and appraisal of the strengths, limitations and implications for research;
• Ethics and research governance processes;
• Systematic and literature reviews;
• Research Methodologies in health care settings;
• Quantitative approaches including statistical analysis;
• Qualitative approaches;
• Mixed Methods;
• The research journey from proposal to completion;
• The roles and responsibilities of the researcher;
• Dissemination of evidence through, publication, posters, conference presentations, journal articles, texts, reports for policy and practice.
Module aims:
The module is the culmination of the student’s postgraduate study and will enable the student to draw on and contribute to the development of the growing body of knowledge in the broad biomedical, clinical, and medical science fields of relevance to the Physician Associate role.
The main aims of the module are to provide students with an understanding of rigorous methods used in systematic reviewing and evidence synthesis and the rationale behind these methods. It will equip students with the essential skills required to carry out a systematic review relating to a range of health care related questions (for example, treatment effectiveness, diagnostic and qualitative research questions).
Module content:
- Assessing patients with complex presentations in specialities such as obstetrics and gynaecology, paediatrics, surgery, acute medicine, psychiatry, musculoskeletal medicine and the elderly
- Carry out an assessment of benefit and risk for the patient starting medication, considering the medication history and potential medication interactions in partnership with the patient and, if appropriate, their relatives, carers or other advocates
- Recognise the challenges of safe prescribing for patients in high-risk groups such as those with long-term conditions, multiple morbidities and medications, in pregnancy, at extremes of age and at the end of life
- Prepare safe and legal prescriptions for a prescriber, tailored to the specific needs of individual patients, using either paper or electronic systems and using decision support tools where necessary. Detect and report adverse medication reactions and therapeutic interactions, appropriately stop or change medication and recognise the risks of over-prescribing. This will include the ethical and legal considerations of preparing a prescription.
Module aims:
This module develops further the student’s knowledge and understanding of the key pharmacological principles in relation to complex and specialist conditions.
The theory and clinical aspect of the course will cover community medicine; general hospital medicine; general surgery; accident and emergency; mental health; obstetrics and gynaecology; and paediatrics (primarily acute setting).
You will sit a national exam at the end of the second year, including a Multiple Choice Question paper and an Objective Structured Clinical Examinations (OSCE).
Beyond the Classroom
You will undertake compulsory placements in:
- community medicine
- emergency department
- general hospital medicine
- general surgical
- mental health
- obstetrics and gynaecology
- paediatrics.
Entry Requirements
2:1 honours degree
We have one intake per year for this course in January. Applications for our January 2025 intake must be made through UCAS. UCAS is the central universities and colleges admissions service responsible for managing applications to higher education courses in the UK. Although this is a Postgraduate course, you will be applying via Undergraduate UCAS.
Applicants should normally have:
- a 2:1 honours degree or above (or accepted equivalent) in life/health sciences, e.g. Medical Science, Biomedical Science, Nursing or one of the Allied Health Professions (Radiography, Radiotherapy, Physiotherapy, etc.).
- a lower second class honours (2:2) degree will only be considered if you have patient facing experience at a professional level (minimum of 1 year).
- successfully passed a minimum of 1 module in human anatomy/physiology at Level 4 (first year undergraduate) or above (a transcript may be requested).
- Applicants whose first language is not English must provide evidence of proficiency to IELTS 7.0 overall, with no less than 6.0 in any band or equivalent.
- Applicants must apply for a Disclosure and Barring Service (DBS) check and Occupational Health check, and register with the Independent Safeguarding Authority.
- Applicants will normally need to demonstrate that they have completed a minimum of 70hrs work experience in a health or social care setting. This experience can be paid employment, voluntary work or job shadowing.
- Acceptance on the course is subject to an assessment interview. Details of our interview dates will be released online soon.
This course is not available to international students.
Fees and Funding
£18,500 for the full course (2024/25)
Guides to the fees for students who wish to commence postgraduate courses in the academic year 2024/25 are available to view on our Postgraduate Taught Programmes Fees page.
This course is not available to international students.
Your course will involve additional costs not covered by your tuition fees. This may include books, printing, photocopying, educational stationery and related materials, specialist clothing, travel to placements, optional field trips and software. Compulsory field trips are covered by your tuition fees.
If you are living away from home during your time at university, you will need to cover costs such as accommodation, food, travel and bills.
The University of Chester supports fair access for students who may need additional support through a range of bursaries and scholarships.
Full details, as well as terms and conditions for all bursaries and scholarships can be found on the Fees & Finance section of our website.
Your future Career
Careers service
The University has an award-winning Careers and Employability service which provides a variety of employability-enhancing experiences; through the curriculum, through employer contact, tailored group sessions, individual information, advice and guidance.
Careers and Employability aims to deliver a service which is inclusive, impartial, welcoming, informed and tailored to your personal goals and aspirations, to enable you to develop as an individual and contribute to the business and community in which you will live and work.
We are here to help you plan your future, make the most of your time at University and to enhance your employability. We provide access to part-time jobs, extra-curricular employability-enhancing workshops and offer practical one-to-one help with career planning, including help with CVs, applications and mock interviews. We also deliver group sessions on career planning within each course and we have a wide range of extensive information covering graduate jobs .